A Simple Blood Test For Early Cancer Diagnostics and Screening
JaxBio is a startup company with the mission of revolutionizing cancer diagnostics and management through the development of a innovative liquid biopsy-based technology. Established in 2021 as a spin-off from Tel-Aviv University, the company was founded by scientists Prof. Yuval Ebenstein and Dr. Shahar Zirkin, along with business experts Dror Feldheim and Joel Bar-El. JaxBio secured $6M in seed round investment and an additional $3M in grants from the EU and Israel Innovation Authority. The team comprises highly qualified Ph.D.-holding biologists, chemists, and data scientists, with an advisory board composed of leading clinicians specializing in oncology, cancer research, and clinical studies.
The Technology:
JaxBio’s proprietary process involves extracting cell-free DNA from the blood, fluorescently labeling biomarkers, and hybridizing them onto a custom high-content microarray. Spots on the array illuminate according to the pattern of the specific DNA sequence. A machine learning algorithm analyzes the unique fluorescent fingerprint to define the type and stage of the disease.
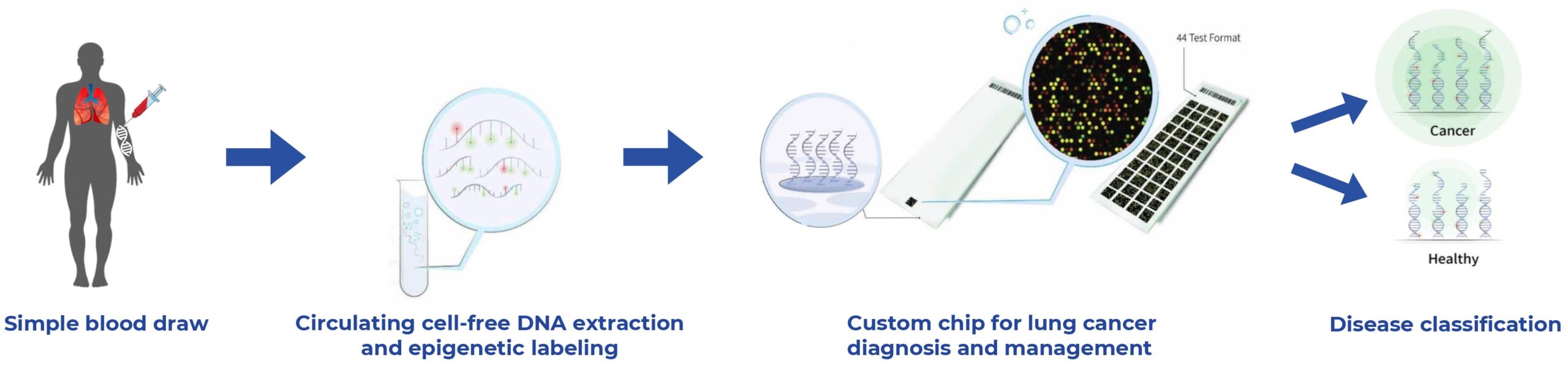
By eliminating the need for sequencing, our new approach is both highly sensitive and cost-effective. Consequently, the test enhances screening and early detection capabilities for cancer, applicable in determining responses to therapy, minimal residual disease detection, and disease management.
The company’s primary focus is currently on developing a diagnostic test for lung cancer as its initial product. Current gold standard imaging-based screening and diagnostics tests frequently provide inconclusive results, necessitating an invasive biopsy that can lead to complications. Furthermore, there is an urgent need for a validated technology to evaluate minimal residual disease post-surgery or therapy. Therefore, a minimally invasive test is urgently needed to detect residual or early-stage lung cancer with high sensitivity. Such a test can complement existing gold standard methods and enhance outcome results by providing a clinical guiding tool.
Analyzing 200 samples, our findings reveal hundreds of distinct genomic loci differentiating between healthy and lung cancer states, as well as classifying histological subtypes. In a blind test, over 90% of the samples were correctly identified (healthy samples as healthy and cancer samples as cancer). Moreover, our test easily distinguished lung cancer samples from stages I and II, indicating the potential sensitivity to detect lung cancer at early stages.
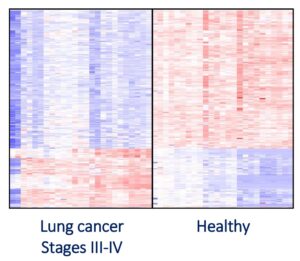
Heat maps presenting methylation levels in differential genomic loci of lung cancer (Red- hypermethylation. Blue- hypomethylation).
JaxBio received a $2M Horizon Europe Cancer Mission grant for the SANGUINE project. The project aims to develop a diagnostic test for early detection of hematological malignancies, response to therapy, and detection of minimal residual disease. Current diagnostic and monitoring procedures for hematological malignancies involve invasive procedures that do not provide sufficient information for effective disease management and treatment. The project involves a robust team of experts from across Europe, specializing in clinical, technological, and social fields. A clinical trial involving 3000 patients has been initiated to develop a custom hematological test for implementation in medical centers across Europe. (clinicaltrials.gov)

In preliminary experiments, we identified a robust biomarker set distinguishing healthy individuals from various hematological malignancies and pre-malignant states. These findings represent a significant advancement in the diagnosis and monitoring of hematological malignancies.
Future Directions:
Our technology is a versatile platform customizable for various diseases, including different types of cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and heart diseases. Our vision for the test extends to diverse applications, including early disease detection, monitoring disease status, and predicting response to therapy, depending solely on the samples used in the development process. Additionally, it can support drug discovery efforts by monitoring treatment response.
